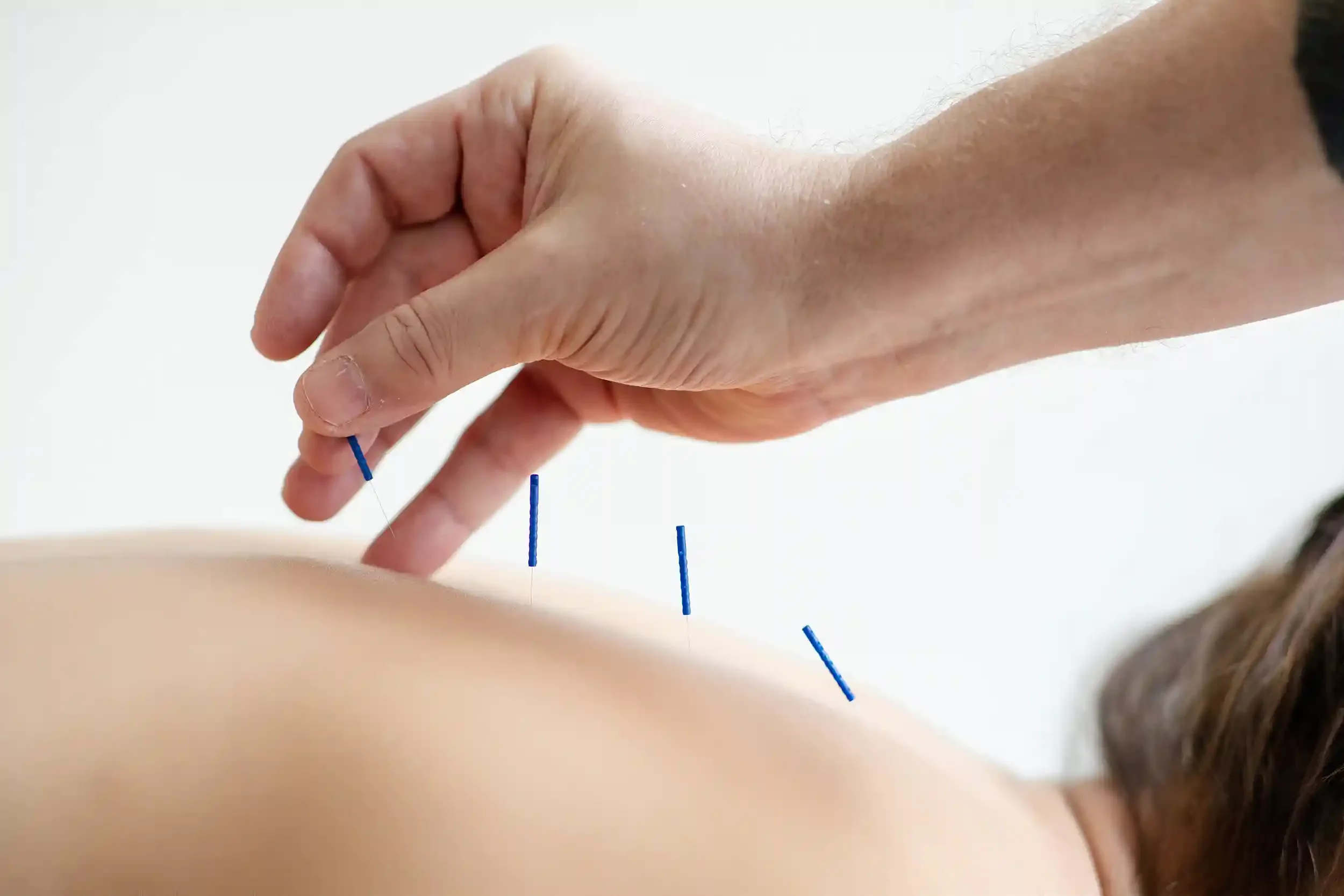
Ancient wisdom for modern maladies.
Grounded in thousands of years of practice, acupuncture is a powerful treatment method within Traditional Chinese Medicine (TCM) that provides incredible therapeutic benefits for dozens of health-related conditions.
How It Works
Acupuncture uses thin, sterile needles carefully placed at specific points to stimulate the nervous system, influence brain activity, and shift how the body processes pain. This process helps release hormones, endorphins, and neurotransmitters, promoting natural pain relief, improved circulation, and overall balance.
Who It Helps
People often turn to acupuncture when conventional medicine falls short – when medications haven’t worked, doctors don’t listen, or they’ve been told to simply live with discomfort. Today, over 54 million people have coverage for acupuncture as an essential health benefit, while even more are covered for acupuncture as a treatment for lower back pain.
“A review of nine studies that compared acupuncture with drug treatment for preventing migraines found that acupuncture was more effective than drugs. In addition, participants who received acupuncture were far less likely to drop out the studies due to severe side effects compared to those receiving drug treatments.”
— National Center for Complementary and Integrative Health 2020
Frequently Asked Questions
-
Yes. Since the mid-1970s when the practice of acupuncture first became popular in the United States, there have been over 10,000 scientific studies investigating acupuncture for the treatment of a wide range of diseases. Many show that acupuncture produces beneficial effects and when combined with conventional treatments, such as pharmaceuticals or physical therapy, it greatly enhances their effectiveness as well. Today, many of the of the most highly rated healthcare institutions in the country including Johns Hopkins Medicine, the Cleveland Clinic, Memorial Sloan Kettering Cancer Center, and the Mayo Clinic have added acupuncture to their treatment centers.
-
Acupuncture has its roots in Traditional Chinese Medicine (TCM), but contemporary acupuncture treatment is also equally informed by modern medicine. Acupuncturists are licensed by the Virginia Board of Medicine, have 4 years of conventional medical training, and have passed a series of rigorous national board exams in both acupuncture and conventional medicine.
-
For most patients, significant improvement can likely be achieved within 8 to 12 treatments. There are a number of factors, however, that can affect recovery time including the length of time the health complaint has been affecting the patient, the complexity of the disease, and a patient’s overall health and age.
-
While acupuncture is generally not considered painful, it should not be considered absolutely painless either. For many conditions, especially musculoskeletal pain, acupuncture works best when the patient experiences some sensation at the local needling site, which is often experienced as tingling, numbness, heaviness, and other feelings of moving energy. This is an indication that the needle has been put in the correct location and will produce the optimum healing effect.
If you are sensitive to acupuncture, we can use very thin gauge needles or small, non-penetrating needles held in place with adhesive tape. These can reduce your sensitivity to allow you to receive a full acupuncture treatment and will still produce a healing effect for your condition.
Want to know more?